

Senior Director of Analytics

Marketing Associate
The Opportunity for Better Testing
We're big fans of Google Optimize, a premium testing and personalisation tool. We're also big fans of Double Blind Testing. Double Blind Testing weeds out the bias that can diminish the effectiveness of your data analysis. This article proposes integrating Double Blind Testing with Google Optimize to further validate your marketing research, thus helping your marketing dollars go further.
What is Double Blind Testing? A handy definition:
A double blind test is an experiment where both the subject and observer are unaware that the exercise in practice is a test. Double blind testing is referred to as the gold standard of testing. Double blind tests are used in science experiments in medicine and psychology, including theoretical and practical testing.
See how that's different from Optimize testing? With Optimize, the analyst often sets up the test, runs the test, analyses the test, calls the winner (if there is one) and shares learnings. That last part of the process, sharing the learnings from the test, is the most important piece.
Caution: Unconscious Bias Ahead
One person wearing multiple hats during testing is also known as a single blind test and comes with consequences. A single blind test risks being influenced by unconscious bias. In a single blind test, the test participant is the only individual unaware of the experiment they're being subjected to. The person running the test knows what is the control and what is the experiment.
There's the rub. It's quite possible for an analyst to draw a conclusion around results based on their knowledge of the test participant - not necessarily to the extent of creating manufactured data, but unconscious bias creeps in subtly.
For example, the analyst may be presented with an aggregated view of the data that shows the experiment outperformed the control. At first, this sounds like a success! However, confirmation bias could make the analyst less likely to dig deeper and explore the data under a more critical lens. With the results in the bag, the analyst moves on and misses important insights into the effects of the experiment.
The opposite is also possible: the control wins, so the experiment tanks. This cannot be true! So the analyst, misled by their cognitive bias, wastes time digging for signals that validate their hypothesis.
Change the Methodology to Remove Bias
Testing is a team effort. Divide [effort across the team] and conquer [cognitive bias] to achieve proper double blind tests. Let's take a look at how a simple A/B test approach might change:
First, the test owner develops the hypothesis, which must remain private to the test owner.
Based on data [a] and feedback [b], we believe that doing [c] for audience [d] will make [e] happen.
We will know this to be true when we observe data [f] and get feedback [g].
We expect a change in metric [h] of magnitude [i] within [j] business cycles.
The test owner will then work with the designer and front end engineer to develop and implement the test experiment. It's important for the test owner to keep the hypothesis a secret and only share what the test experiment is with other team members. The reason for the test should not be revealed.
The test is executed and now an analyst is introduced to the test data. The analyst has no previous knowledge of the hypothesis, experiment design or testing process at all. They only know this is a test in which they must perform a calculation on the presented data to determine the test experiment performance and significance.
Setting Up a Double Blind Test
Tell your data engineers to get the Google Analytics add-on for Google Sheets. Share the audience definition piece of the hypothesis with the data engineer. The data engineer will set up a query as shown below to produce two reports accurately representing the audience defined in the hypothesis. One report is the daily session, conversion volume and conversion rate for the test experiment. The other report is for the control. Name the report Population A and B - something anonymous will work.
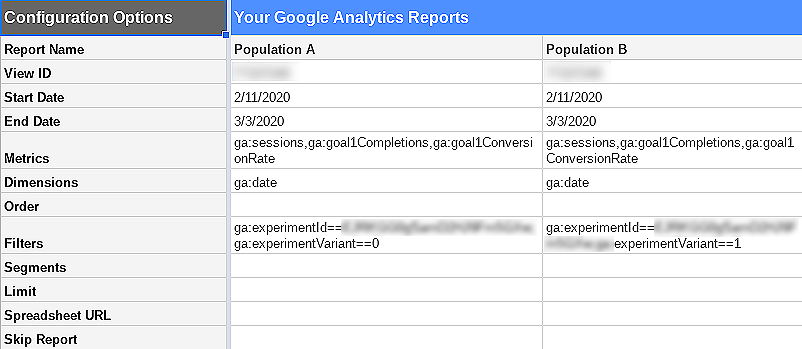
Now schedule the report to refresh daily. Having done this, hide the config sheet and make sure the test analyst is not given editor rights on the data so they cannot see the produced report config:

Now the analyst has blind access to the data with no awareness of what the experiments are for, what the hypothesised effect is, who the audiences are or which population corresponds with what experiment. Due to the blind data access, there is no cognitive bias in the analysis.
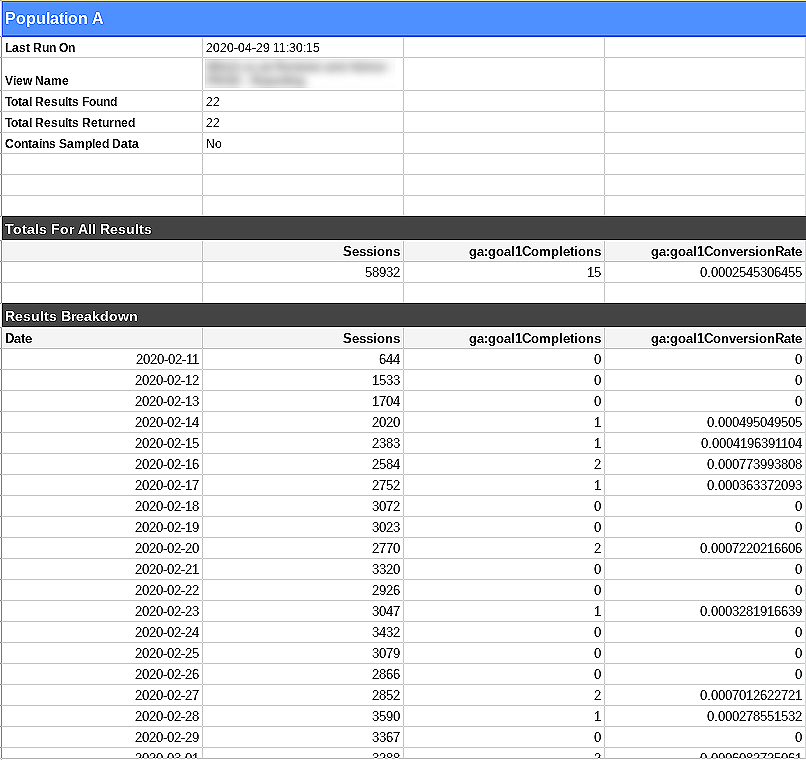
The analyst reports on the performance of each population as they see it in the numbers. Each member of the team is sufficiently removed from the hypothesis and test detail so as to achieve a double blind test production and analysis. Insert happy-dance here!
Integrate into Your Data Team's Workflow
Google Optimize just leveled up by going one step further with Double Blind Testing. The double blind testing strategy has the power to improve your data analysis. It can open opportunities for you and your team by decreasing unconscious bias and increasing the effectiveness of your media spend. Choose to take more control of your marketing dollars by integrating this testing process into your daily workflow.
To learn more about Google Optimize and Double Blind Testing, reach out to us at questions@mightyhive.com.